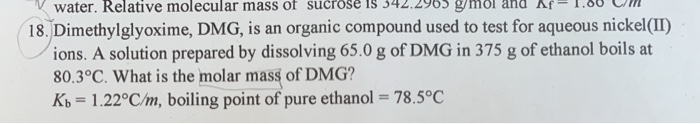| Physical Chemistry Virtual Lab Physical chemistry (also called physicochemistry) is the explanation of macroscopic, microscopic, atomic, subatomic, and particulate phenomena in chemical systems in terms of physical concepts; sometimes using the principles, practices and concepts of physics like thermodynamics, quantum chemistry, statistical mechanics and dynamics. Spectrophotometry || Cryoscopy || Ebullioscopy || EMF measurement || Determination of Viscosity of Organic Solvents || Adsorption Isotherm || Verification of Tafel Equation || Determination of Viscosity Average Molecular Weight of Polymer || Calorimetry -Water equivalent Calorimetry || Calorimetry -Heat of Neutralization |
| Organic Chemistry Virtual Lab Organic chemistry is a discipline within chemistry which involves the scientific study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation (by synthesis or by other means) of chemical compounds that contain carbon. Detection of Functional Groups || Detection of Elements: Lassaigne鈥檚 Test || Separation of Compounds Using Column Chromatography || Purification by Fractional distillation/crystallisation || Purification by Steam distillation/crystallisation || Laser Flash Photometer || Organic Preparations - Allylation of Isatin || Estimation of Aspirin || Estimation Of Glucose || Calculation of 位max of Organic Compounds Using Woodward Fieser Rules |
| Inorganic Chemistry Virtual Lab Inorganic chemistry is the branch of chemistry concerned with the properties and behavior of inorganic compounds. This field covers all chemical compounds except the myriad organic compounds (carbon based compounds, usually containing C-H bonds). Water analysis-Determination of Physical parameters || Water analysis-Determination of Chemical parameters || Acid Base Titration || Gravimetric Estimation of Barium || Gravimetric Estimation of Nickel || Crystal Field Theory || Group Theory || Alloy Analysis (Brass) || Soil Analysis-Determination of Specific conductivity of Soil || Soil Analysis-Determination of pH of Soil |
| Advanced Analytical Chemistry Virtual Lab Analytical chemistry is the branch of chemistry concerned with studying the properties of materials and development of tools used to analyze materials. It is the science of sampling, defining, isolating , concentrating and preserving samples. Soil Analysis-Determination of Available Organic Carbon content in the Soil || Soil Analysis-Determination of Available Nitrogen content in the Soil by Kjeldahl method || Soil Analysis-Determination of Available Phosphorus content in the Soil by Bray's method || Electrogravimetric Estimation of Metals || Estimation of Phosphate Content in Soft Drinks || Flame Photometry || Polarography - Determination of Unknown Concentration of Cadmium || Polarography - Determination of Unknown Concentration of Vitamin C |
To demonstrate a positive test, test a nickel coin. It contains 25% nickel and will turn the swab pink indicating nickel is detected. Nickel Alert can be used to retest items coated with Nickel Guard ™ to verify protective barrier is in place. Nickel Alert should be used in well-ventilated areas.
Also found in: Dictionary, Thesaurus, Acronyms, Wikipedia.- The reagents in use today^ dim®thylglyoxia© probably ap» proaches most closely th© idtal organic analytic precipitant. It is specific for nickel and palladiim, fonsing with each an insoluble compound, fhe specificity of this reagent, however, Is not fully understood. Since nickel dlia«thylglyoxiiB@ can b@ prepared in a.
- Dec 01, 1977 The dimethylglyoxime test for detection of nickel, first described by Fleigl 1 and modified by Fisher, 2 consists of adding a few drops of 1% dimethylglyoxime in alcoholic solution and a few drops of 10% ammonium hydroxide solution to a test object and observing for the presence of a red precipitate. In our modification of this procedure, a few.
dimethylglyoxime
[‚dī¦meth·əl·glī′äk‚sīm] (organic chemistry)
(organic chemistry) 
Dimethylglyoxime
diacetyl dioxime:
Colorless crystals; melting point, 238°-240°C. It is soluble in alcohol, ether, and solutions of alkalies. With nickel salts it yields a red insoluble precipitate of nickel dimethylglyoximate, (C4H7O2N)2Ni, which is a chelate compound. Because of this, dimethylglyoxime is used for the qualitative and quantitative determination of nickel. In 1905, L. A. Chugaev suggested the use of dimethylglyoxime as a specific reagent for nickel. Dimethylglyoxime is made by treating diacetyl with hydroxylamine.
Want to thank TFD for its existence? Tell a friend about us, add a link to this page, or visit the webmaster's page for free fun content.
Link to this page:
Dimethylglyoxime Dmg Is An Organic Compound Used To Test Car