- Jul 30, 2018 By default, it does not allow you to install applications from unidentified developers. However, besides the many malicious apps that can be found in the unidentified-developer-apps category, there are many quality ones. So, the odds are that sooner or later you would probably need to install some apps from unidentified developers on your Mac.
- Jul 20, 2019 How to Install Software from Unsigned Developers on a Mac. This wikiHow teaches you how to install software that isn't approved by Apple on your Mac. MacOS Sierra marks most unofficial apps as unsigned software, so you'll need to perform.
Subscribing will provide email updates when this Article is updated. Login is required. Subscribe Unsubscribe from this article.
The safest place to get apps for your Mac is the App Store. Apple reviews each app in the App Store before it’s accepted and signs it to ensure that it hasn’t been tampered with or altered. If there’s ever a problem with an app, Apple can quickly remove it from the store.
If you download and install apps from the internet or directly from a developer, macOS continues to protect your Mac. When you install Mac apps, plug-ins, and installer packages from outside the App Store, macOS checks the Developer ID signature to verify that the software is from an identified developer and that it has not been altered. By default, macOS Catalina also requires software to be notarized, so you can be confident that the software you run on your Mac doesn't contain known malware. Before opening downloaded software for the first time, macOS requests your approval to make sure you aren’t misled into running software you didn’t expect.
Running software that hasn’t been signed and notarized may expose your computer and personal information to malware that can harm your Mac or compromise your privacy.
View the app security settings on your Mac
By default, the security and privacy preferences of your Mac are set to allow apps from the App Store and identified developers. For additional security, you can chose to allow only apps from the App Store.
Install Dmg From Unidentified Developer Jobs
In System Preferences, click Security & Privacy, then click General. Click the lock and enter your password to make changes. Select App Store under the header “Allow apps downloaded from.”
Open a developer-signed or notarized app
If your Mac is set to allow apps from the App Store and identified developers, the first time that you launch a new app, your Mac asks if you’re sure you want to open it.
An app that has been notarized by Apple indicates that Apple checked it for malicious software and none was detected:
Prior to macOS Catalina, opening an app that hasn't been notarized shows a yellow warning icon and asks if you're sure you want to open it:
If you see a warning message and can’t install an app
If you have set your Mac to allow apps only from the App Store and you try to install an app from elsewhere, your Mac will say that the app can't be opened because it was not downloaded from the App Store.*
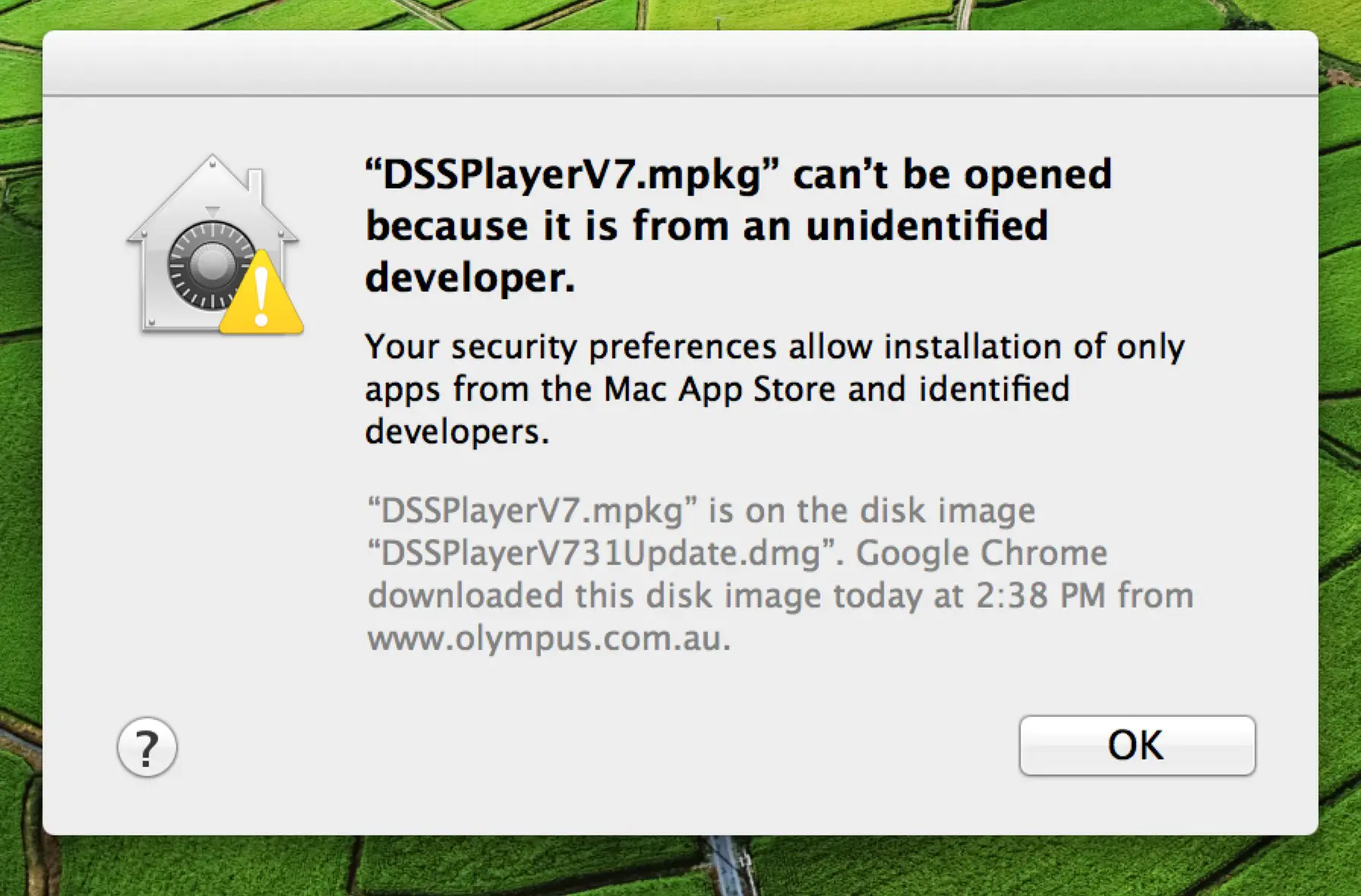
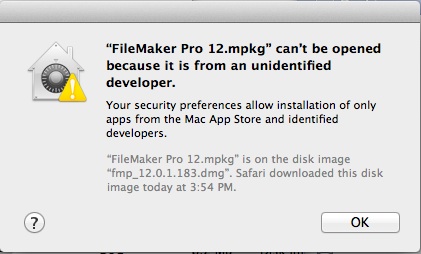
If your Mac is set to allow apps from the App Store and identified developers, and you try to install an app that isn’t signed by an identified developer or—in macOS Catalina—notarized by Apple, you also see a warning that the app cannot be opened.
If you see this warning, it means that the app was not notarized, and Apple could not scan the app for known malicious software.
You may want to look for an updated version of the app in the App Store or look for an alternative app.
If macOS detects a malicious app
If macOS detects that an app has malicious content, it will notify you when you try to open it and ask you to move it to the Trash.
How to open an app that hasn’t been notarized or is from an unidentified developer
Running software that hasn’t been signed and notarized may expose your computer and personal information to malware that can harm your Mac or compromise your privacy. If you’re certain that an app you want to install is from a trustworthy source and hasn’t been tampered with, you can temporarily override your Mac security settings to open it.
In macOS Catalina and macOS Mojave, when an app fails to install because it hasn’t been notarized or is from an unidentified developer, it will appear in System Preferences > Security & Privacy, under the General tab. Click Open Anyway to confirm your intent to open or install the app.
The warning prompt reappears, and you can click Open.*
The app is now saved as an exception to your security settings, and you can open it in the future by double-clicking it, just as you can any authorized app.
*If you're prompted to open Finder: control-click the app in Finder, choose Open from the menu, and then click Open in the dialog that appears. Enter your admin name and password to open the app.
Over the years, Apple has put its vast resources into making it's operating systems more secure for end-users. In macOS Catalina, the company has taken this to all-new levels by introducing beneficial security changes that make it even harder for miscreants to play havoc with our computers. However, because security is a tricky business, so-called improvements for some might not work for others. Specifically, Apple's decision to make Gatekeeper even more difficult crack is a significant step forward for everyday Mac users. For developers, perhaps not so much. Luckily, there's a workaround.
Warning: This terminal trick disables important security aspects of Gatekeeper, which leaves your Mac vulnerable to malware. We highly recommend you reinable the default security settings if you chose to follow this guide at your own risk.
What is Gatekeeper?
Gatekeeper has been an essential part of macOS for years. As its name suggests, the tool has been designed to check recently downloaded apps for known malware and sends it to quarantine. In his June article, The Great Mac Balancing Act, Rene Ritchie explains:
Currently, when you download an app, whether it's off the Store or the Web or even from AirDrop, that app is quarantined. If and when you try to open a quarantined app, Gatekeeper checks it for known malware, validates the developer signature to make sure it hasn't been tampered with, makes sure it's allowed to run, for example matches your settings for App Store apps and/or known developer apps, and then double checks with you that you really want to run the app for the first time, that it's not trying to pull a fast one and autorun itself.
Until now, Gatekeeper didn't take the same approach with apps launched via Terminal. It also didn't check non-quarantined apps and files for malware. In other words, it checked an app only once for malware.
Significant changes have arrived with macOS Catalina.
Now, apps started through Terminal are also checked. These files get the same malware scan, signature check, and local security policy check. The difference: even on the first run, you only need to explicitly approve software launched in bundles, like a standard Mac app bundle, not for standalone executables or libraries.
With macOS Catalina, perhaps more significantly, Gatekeeper will also check non-quarantined apps and files for problems. Not just once or twice, but every time you run it. When your Mac detects a problem, it blocks the file, then sends you an alert.
If all this sounds fantastic to you, terrific. That's undoubtedly Apple's intent. However, some developers might view this differently and find the changes cumbersome, at best.
A Workaround
Even though Gatekeeper in macOS is now stricter than ever, there is a way around it -- including macOS Catalina's newest tools. The workaround makes it possible to download and use apps downloaded from anywhere on macOS Catalina and earlier versions without a check.
First published in 2016 by OSX Daily, but still valid, the 'fix' works like this:
- Be sure to exit System Preferences on your Mac.
- On Finder, click Go.
- Select Utilities.
Double-click Terminal.
- Type of the following command syntax:
sudo spctl --master-disable. - Hit Return
- Authenticate with an admin password.
- Hit Return.
- Exit Terminal.
Changing your settings
Now, it's time to allow your Mac to open any app.
- Click on System Preferences on your Mac Dock.
- Choose Security & Privacy.
Tap the lock at the bottom left of the screen.
- Enter your password to unlock Security and Privacy.
- Choose the Anywhere under Allow apps downloaded from. Prior to making the change, this option wasn't available.
Click the unlocked lock to keep the change.
With this change, Gatekeeper no longer monitors your computer for malware coming from apps and files.
Restoring to the original setting
If you'd like to return to the default Gatekeeper settings, perform these steps:
- Be sure to exit System Preferences on your Mac.
- On Finder, click Go.
- Select Utilities.
Double-click Terminal.
- Type of the following command syntax:
sudo spctl --master-enable. - Hit Return
- Authenticate with an admin password.
- Hit Return.
- Exit Terminal.
Install Dmg From Unidentified Developer Windows 10
View the change
To confirm your Mac has returned to the default settings:
- Click on System Preferences on your Mac Dock.
- Choose Security & Privacy.
Under Allow apps downloaded from, notice the select is now App Store and identified developers.
Should you make this switch?
For nearly every Mac user, there's no reason to make the listed change under Security & Privacy on macOS Catalina. It should only be performed if you can quickly determine whether apps are legitimate or not. Keep this in mind.
Questions?
If you have any questions or concerns about Gatekeeper or the rest of the macOS Catalina update, let us know in the comments below.
Install Dmg From Unidentified Developer Free
macOS Catalina
Main
Install Dmg From Unidentified Developer Mac
leakedInstall Dmg From Unidentified Developers
iPhone 9 and the next iPad Pro confirmed in iOS 14
Apple's iPhone 9, as well as the iPad Pro, AirTags and a new Apple TV remote, have all been spotted in iOS 14.